Axis Aligned Artifacts for Robust Random Cut Forests
There are artifacts created by choosing axis aligned cuts in robust random cut forests, similar to what was noted with IsoForest..
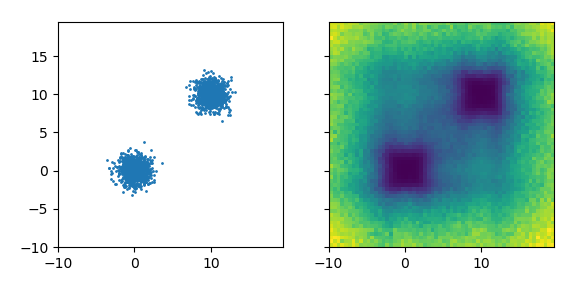
Left: Original data distribution. Right: Learned co-displacement, darker is lower.
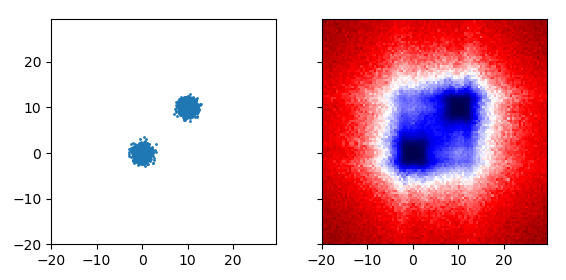
Notice the echoes around (10,-10) and (-10, 10)
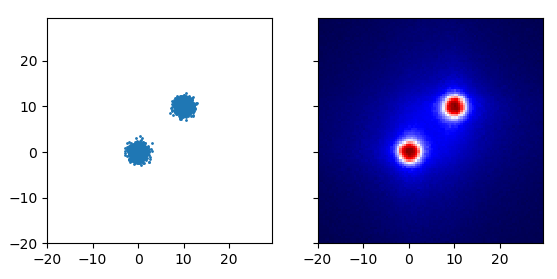
If instead of either of these, you use the depth in the robust random cut forest, you get what’s shown above. The first two examples are recreated by the code below:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import rrcf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
include_anomaly=False
# Construct data with two modes and full of anomalies
X1 = np.random.([0,0], [[1,0],[0,1]], 1000)
X2 = np.random.([10,10], [[1,0],[0,1]], 1000)
if include_anomaly:
XA = np.random.(-5, 15, size=200).((100, 2))
X = np.([,,])
else:
X = np.([,])
# plot the original data
fig, ax = plt.()
ax.([:,0],[:,1], '.')
fig.()
num_trees = 300
tree_size = 256
n = X.[0]
# Construct forest
forest = []
while len() < num_trees:
# Select random subsets of points uniformly from point set
ixs = np.random.(, size=( //,),
replace=False)
# Add sampled trees to forest
trees = [rrcf.([], index_labels=) for ix in ixs]
forest.()
# prepare grid for codisp measurement
xvals, yvals = np.(-10, 20, 0.5), np.(-10, 20, 0.5)
nx, ny = len(), len()
xv, yv = np.(,)
codisp = np.((,))
# measure codisp across space
for i in range():
for j in range():
temp = []
for tree in forest:
point = np.([[,],[,]])
tree.(, index='test')
temp.(.('test'))
tree.('test')
[,] = np.()
# plot codisp
fig, axs = plt.(ncols=2, sharex=True, sharey=True)
[0].([:,0],[:,1], '.', ms=2)
[0].(1)
[1].(, origin='lower',
extent = [.(),.(),.(),.()])
fig.()
fig.("bias.png")